Defense Drone Problem
Battery-powered drones cannot complete vital missions

With an average flight time under 30 minutes, battery-powered drones and sUAS platforms cannot complete long and variable-duration missions
Battery limitations prevent drone support for missions involving ISR (intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance), security, emergency response and tactical communications.
On-ground recharging results in long downtimes, a critical risk for safety-related missions.
Defense Drone Solution
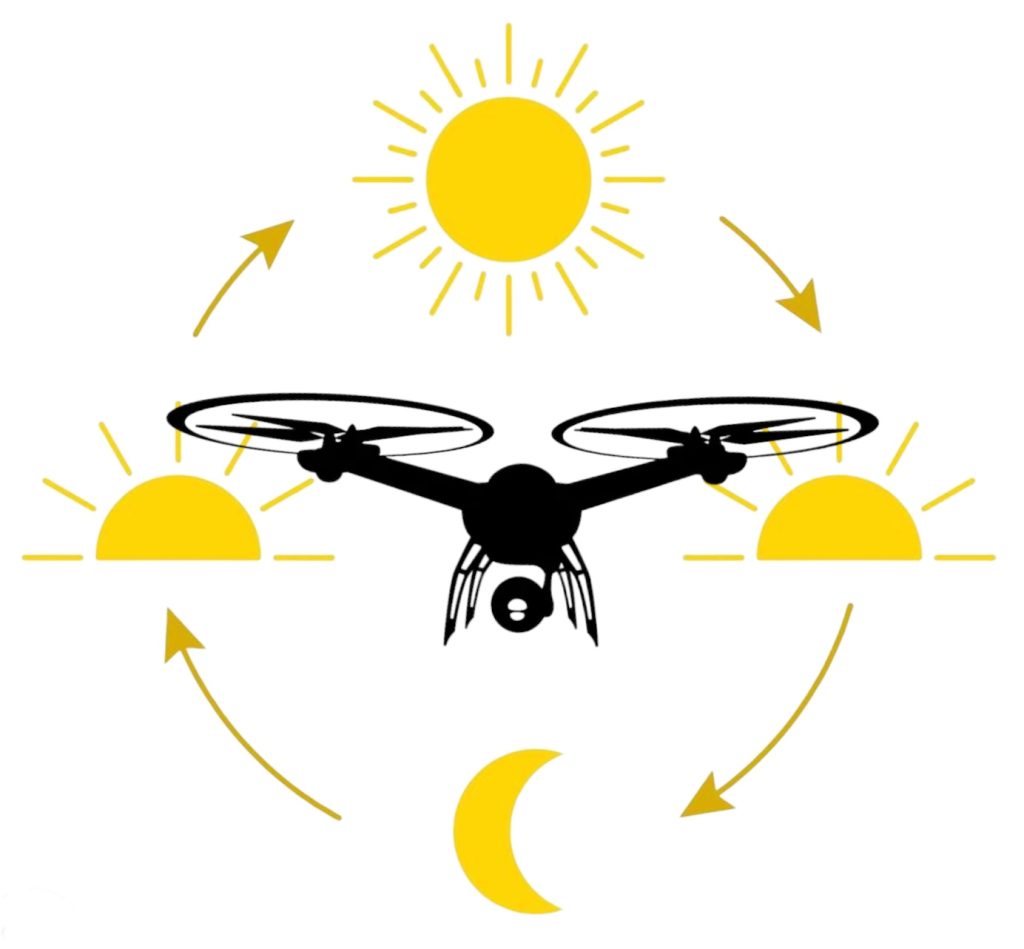
AeroCharge Long-Range Wireless Power allows drones to fly CONTINUOUSLY
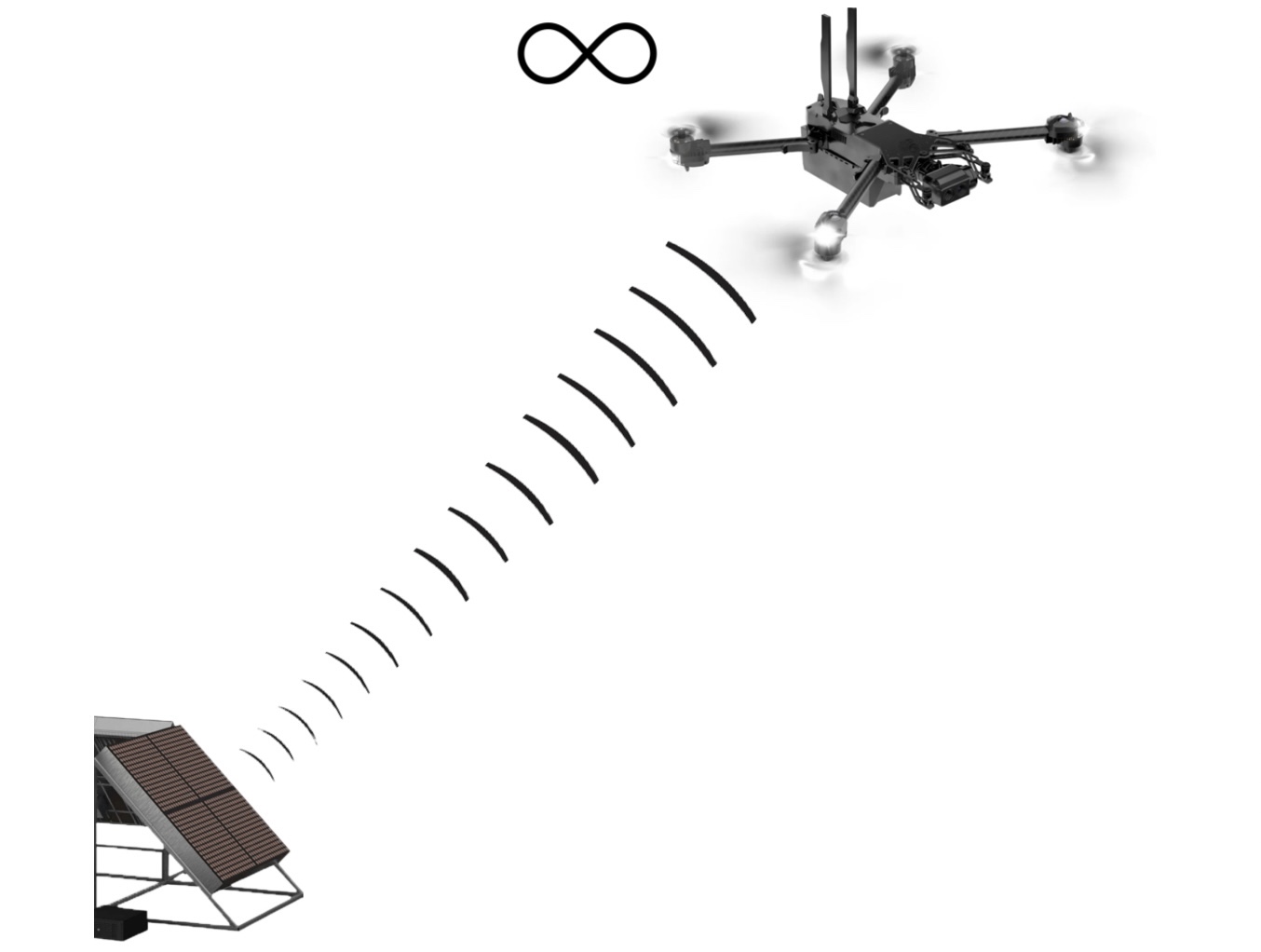
Persistent Power | Extended Range | Automatic Targeting | In-Flight Recharging
When integrated with a long-range wireless power system from AeroCharge, a battery-powered drone can fly autonomously for many hours without landing.
The ground transmitter uses RF power beaming to generate power and steer it to a device. The receiver collects the energy and powers the device while in operation.

AeroCharge wireless power transmission allows drones to fly out of range of the power beam and return for in-flight charging.

Line of sight is not needed to transmit and receive power. The beam can travel through plastic, glass, cardboard and other materials.

Current Development
| Delivered Power | 1000 Watts |
| Max Transmit Distance | 100 meters |
| Antenna Array Diameter | up to 1 meter |
| Target Receiver Efficiency | up to 70% |
| Receiver Output Voltage | up to 24V |
| Frequency | Upon Request |
| Other Features | Dynamic drone tracking Dynamic power delivery Automated beam steering High-precision beam pointing |
AeroCharge wireless power transfer outperforms tethered drones

| AeroCharge Wireless Power | Feature | Tethered Drone |
|---|---|---|
| Yes | Continuous power from ground source | Yes |
| Yes | Drone can fly beyond ground power range | No |
| Yes | Power transmission method conceals source location | No |
| Yes | Maneuverable in dense environments (urban/forest/jungle) | No |
Product Integration
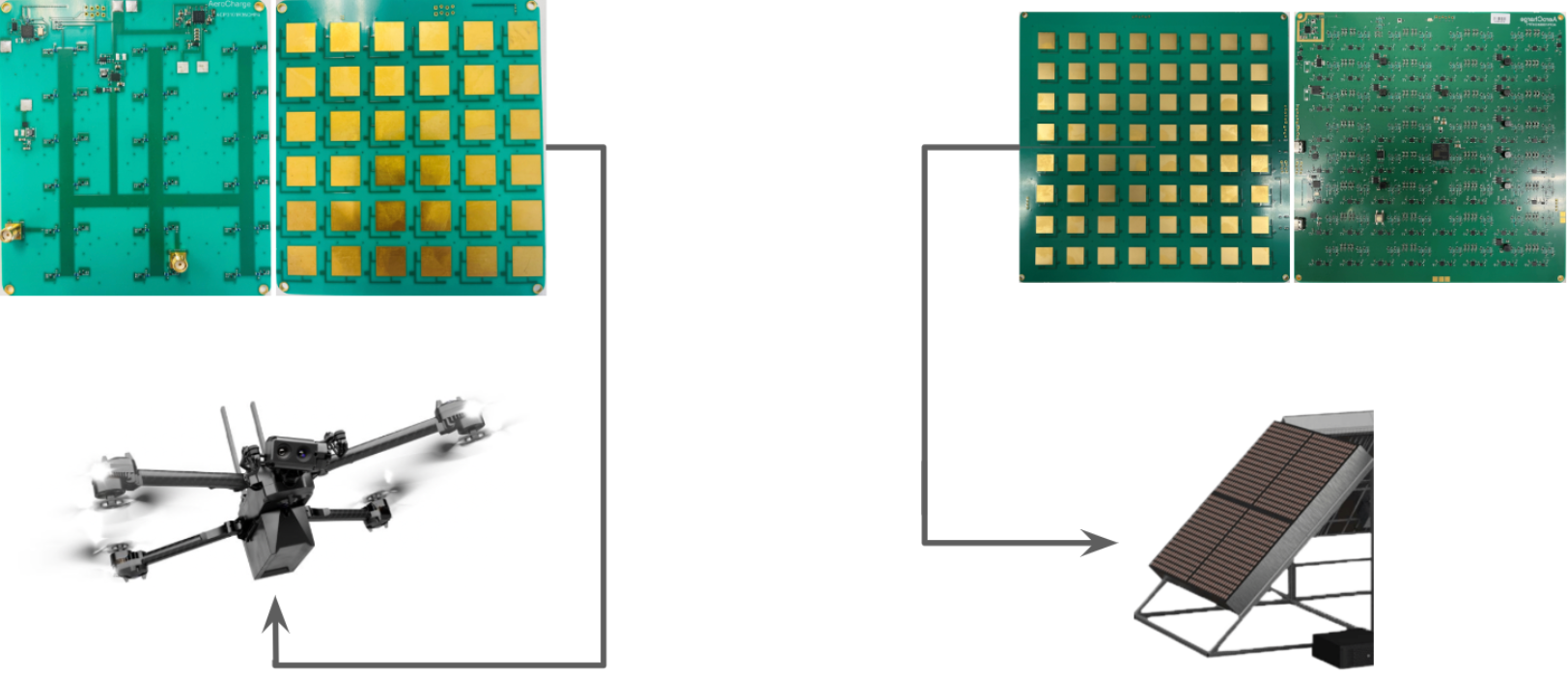
1. Phased-array antenna power transmitter and rectenna receiver are designed to meet requirements for each sUAS platform
2. Receiver integrates into underside of drone to receive power and charge battery
3. Transmitter is paired with receiver to conduct continuous wireless energy transfer using RF power beaming
Use Cases

Force Protection
Defense ISR
HMI Formations

Facility Security

Emergency Response

Energy Relay

Search and Rescue

Tactical Communications

